How to use PBN backlinks to boost website ranking
Category : Link building
Using PBNs, you can get fantastic links, fast. If you stick to the standard link building strategies like outreach, for instance, it might take you longer (frequently, more expensive) to receive backlinks. In addition, if you have 2 or more money websites, you can use your PBNs to promote them all (carefully, of course).
Why Private blog networks are so powerful? Because you’re using the authority of the already established, older websites. They have been around for a while. Backlinks from sites like these are great for your SEO.
A PBN allows you to source high-quality backlinks in bigger quantities, without the hassle and time-consuming process of conventional link building.
People who use a PBN will likely create large website networks whilst the domain is under their control. They will then link to with a nice velocity ‘naturally’ rise in the search engines rankings.
By using an aged domain, you will be able to successfully transfer a large amount of strength to your own domain or website from the past links that domain has accumulated. This ‘link strength’ is similar to a ranking power, allowing an older domain to pass on more ranking power than a new website. This is mainly because older domains carry more authority than newer ones. This is often referred to as ‘link juice’ in the SEO community, but it’s important to look at the quality of the links as well. Often an expired domain will be heavily spammed so and it might look very powerful in tools like Ahrefs but in fact, it’s quite toxic.
If you want your website to be ranking at the top of the Google search engine, you will require a lot of strong high-quality backlinks to it. With a PBN, you have complete control of the link as you own the main website it is linking to. This allows you to choose the ideal anchor text, content and placement of the link within your site.
Once you have a PBN website functioning and linked to your money making site, you will have a general understanding of the costs involved.
You know that it takes approximately $XX and Y hours to create one link. With this data you can then scale up to your desired amount of links, allowing you to have an almost exact costing framework to go by for the future. This is very dependent on how you build your PBNs, everyone has their own strategy but we share our strategy further on.
It is recommended that you start linking to your money site from your PBN when it feels natural to do so. This means, if you have a money site that has little or no links from any other sites, then it is not recommended to start sending your PBN links to your site as yet.
If your site has backlinks from other sources, such as outreach or guest posts, and the anchor texts from the links are varied, then it a good time to drip-feed PBN links to your money making site.
The main reason your money site needs backlinks before you start drip-feeding PBN links is that you want to avoid the anchor texts density from becoming unnaturally high.
The way to use PBN backlinks
It is crucial to use your PBN links effectively and strategically. The best links your site will get are from your PBN links. This is because you have complete control over link equity, anchor texts, and you can link from more powerful pages. You will need to blend your PBN links with any other links on your site to ensure you pass any manual reviews.
Without doing the above, your PBN could be at risk which could jeopardise your money site.
I recommend you do not start link building from your PBN to your money site immediately. Only once you have a domain that is indexed, ranked for its naked domain name and you have included links to an authority site, should you then create a page related to your money site and link it back to that. Be sure to check all the backlinks to the domain, selecting the page with the most high-quality backlinks. Thereafter you can add the link to your money making site to ensure you get maximum output. Adding links to between the pages internally will also quietly help your link, and encourage easy flow to and from your webpage. In most cases I’d recommend waiting 30-60 days to link to your money site after building your PBN site (this means getting content and getting the new version of the website indexed).
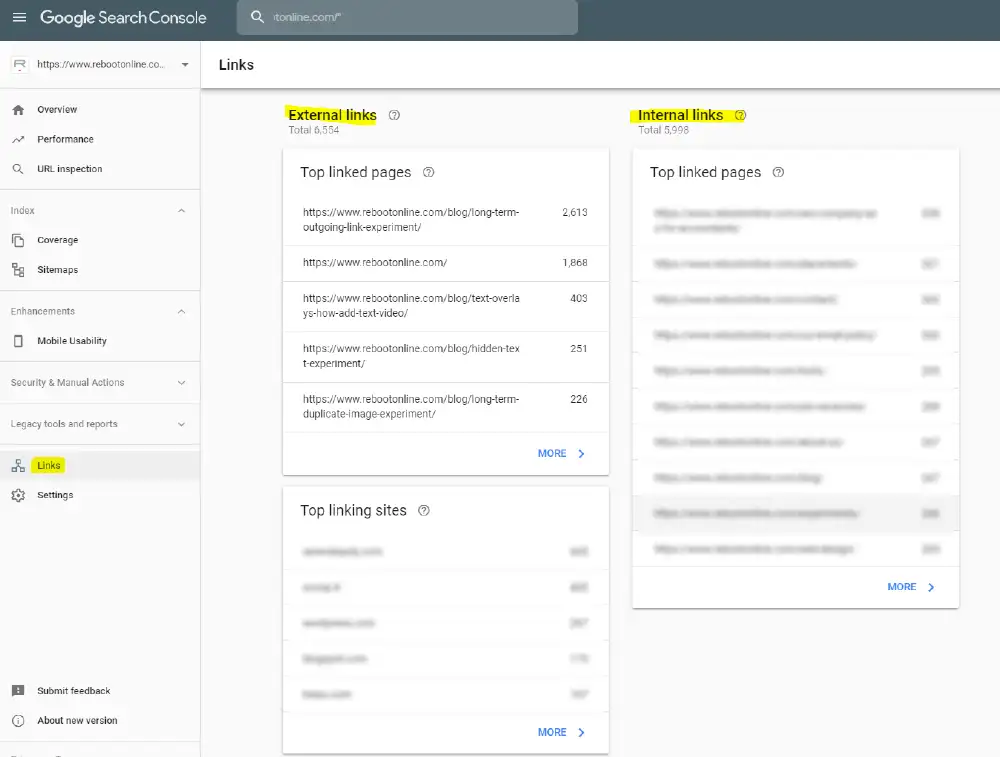
There are two things that make a PBN powerful and this goes for pretty much any type of link you ever build. That is relevance and/or authority. These are the two things you are looking for when picking a domain. Now would be a good time to point out that you need to be analyzing the 5 year index and not the 90 day index to get a real understanding of a domain. That’s why a majority of my domains have very few referring domains in the 90 day index as they did.
Read more How many backlinks per day are enough for keyword ranking?
_______________________________________________________________________________
Please contact us for seo service packages at TDHSEO.COM.
TDHSEO Team
Email: tdhseo@gmail.com
Skype: tdhseo
https://www.facebook.com/tdhseo
Thank you!