After Fred rolled out, it was clear that it was a significant core ranking update tied to quality. If you’ve read my previous posts about Google’s major core ranking updates, you will see many mentions of aggressive monetization, advertising overload, etc. Well, Fred seemed to pump up the volume when it comes to aggressive monetization. Many sites that were aggressively monetizing content at the expense of users got hit hard.
With that quick intro out of the way, let’s hop into specific examples of impact from Fred update
Example1 – Getting smoked.
A major hit based on UX Barriers, aggressive monetization, and low quality user experience.
The first two examples detailed a major surge and then a site dealing with the gray area of Google’s quality algorithms. Now it’s time to enter the dark side of Fred. There are many sites that got hammered by the 3/7 update, with some losing over 50% of their Google organic traffic overnight (and some lost up to 90%).
The next site I’m going to cover has dealt with Panda and major core ranking updates in the past. It’s a relatively large site, in a competitive niche, and is heavily advertising-based from a monetization standpoint.
When Fred rolled through, the site lost over 60% of its Google organic traffic overnight. And with Google representing a majority of its traffic, the site’s revenue was clearly hit hard. It’s also worth noting that Google organic traffic has dropped even further since 3/7 (and is down approximately 70% since Fred rolled out.)
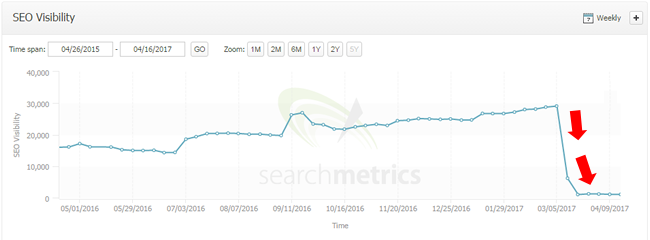
UX Barriers Galore
If you’ve read my previous posts about Google’s major core ranking updates focused on quality, then you’ve seen many examples of what I call “low quality user engagement”. Well, this site had many problems leading up to the 3/7 update. For example, there were large video ads smack in the middle of the content, deceptive ads that looked like download buttons (which users could mistakenly click thinking they were real download buttons), flash elements that don’t load and just display a shell, and more.
And expanding on the deception point from above, there were links in the main content that looked like internal links, but instead, those links whisked users off to third party advertiser sites. Like I’ve said a thousand times before, “hell hath no fury like a user scorned”. And it looks like Fred had their back.
To add insult to injury, the site isn’t even mobile-friendly. When testing the site on a mobile device, the content is hard to see, it’s hard to navigate around the site, etc. Needless to say, this isn’t helping matters. I can only imagine the horrible signals users are sending Google about the site after visiting from the search results.
This is why it’s so important to analyze your site through the lens of these algorithm updates. Understand all “low quality user engagement” problems riddling your site, weed them out, and improve quality significantly. That’s exactly what Google’s John Mueller has been saying when asked about these updates (including Fred).

Example 2 – Tired of the gray area. Better late than never.
The next example I’m going to cover is a large-scale site driving a lot of traffic from Google organic historically. The site has been in the gray area of Google’s quality algorithms for a long time and has seen major drops and surges over time.
The company finally got tired of sitting in the gray area (which is maddening), and decided to conduct a full-blown quality audit to identify, and then fix, “low quality user engagement” problems. They began working on this in the fall of 2016 and a number of the changes did not hit the site until early 2017. In addition, there are still many changes that need to be implemented. Basically, they are in the beginning stages of fixing many quality problems.
As you can see below, the site has previously dealt with Google’s major core ranking updates focused on quality. Here’s a big hit during Phantom 2 in May of 2015, and then recovery during the November 2015 update:
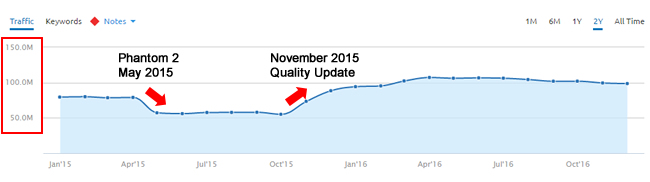
When a site is in the gray area of Google’s quality algorithms, it can see impact with each major update. For example, it might drop by 20% one update, only to surge 30% during the next. But then it might get smoked by another update, and then regain some of the losses during the next. I’ve always said that they gray area is a maddening place to live.
When Fred rolled out on 3/7/17, the site dropped by approximately 150K sessions per day from Google organic. Now, the site drives a lot of traffic so that wasn’t a massive drop for them. But it also wasn’t negligible. In addition, the site increased during the early January update, so the company was expecting more upward movement, and not less.
Here’s a close-up view of the drop. More about the second half of that screenshot soon (not shown).
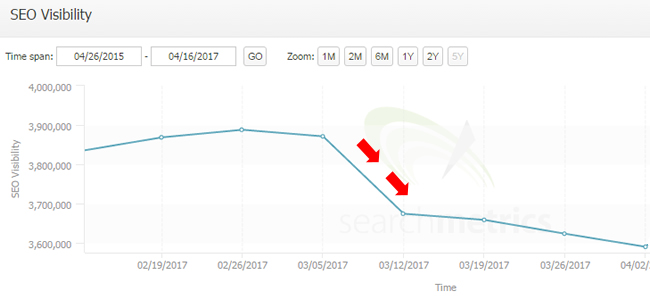
It can be frustrating for site owners working hard on improving quality to see a downturn, but you need to be realistic. Even though the site has a lot of high quality content, it also has a ton of quality issues. I’ve sent numerous deliverables through to this company containing problems to address and fix. Some of those changes have been rolled out, while others have not. Currently, there are still many things to fix from a quality perspective.
Example 3 – Soaring With Fred
The first example covers an amazing case study. It’s a site I’ve helped extensively over the years from a quality standpoint, since it had been impacted by Panda and Phantom in the past. It has surely seen its share of ups and downs based on major algorithm updates.
When Fred rolled out, it didn’t take long for the site owner to reach out to me in a state of Google excitement.
“Seeing big gains today. Traffic levels I haven’t seen in a long time… Is this going to last??”
Needless to say, I immediately dug in.
What I saw was a thing of beauty. It was a surge so strong that it would make any SEO smile. The site literally jumped 125% overnight (and this isn’t a small site with a minimal amount of traffic). Google organic surged by 110K sessions per day and has remained at that level ever since. Here are screenshots from Google Analytics and Google Search Console:
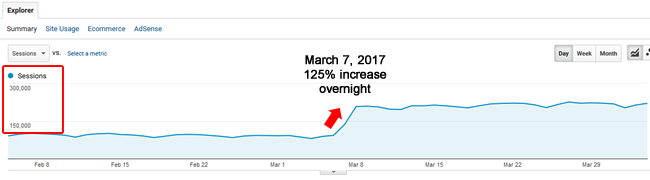
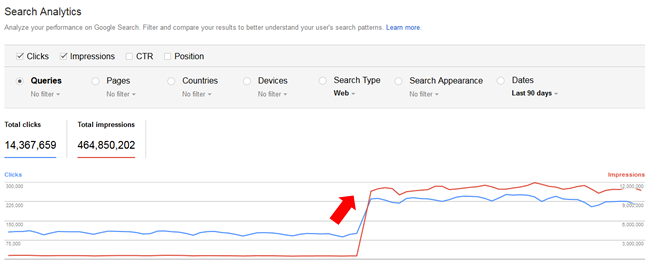
Reviewing the audits I performed for the site revealed many low quality content problems and “low quality user engagement” barriers. And that included aggressive monetization. So the remediation plan covered an anti-Panda and anti-Phantom strategy.
Read more Something important about Google algorithm update
_______________________________________________________________________________
Please contact us for seo service packages at TDHSEO.COM.
TDHSEO Team
Email: tdhseo@gmail.com
Skype: tdhseo
https://www.facebook.com/tdhseo
Thank you!